[Food Safety & You] Food Allergy vs. Food Intolerance
February 23, 2022
blog

Definition
- Food allergy refers to the medical condition in which the body’s immune system mistakenly treats proteins in certain food as a threat, and hence, proceed to defend with immune reactions
- Food intolerance refers to the difficulty our digestive system has with digesting certain foods which results in an unpleasant physical reaction
Cause / Trigger
Food allergy
- Food allergy is induced by proteins presented in specific food items.
- Majority of food allergies are caused by 8 common food categories:
- Milk
- Egg
- Soy
- Wheat
- Peanuts
- Tree nuts e.g. almond, cashew, etc.
- Fish
- Shellfish e.g. prawns, crabs, etc.
- The consumption or even just physical contact with small traces of these allergens may already trigger a reaction
Food intolerance
- Food intolerance can be caused by a much wider spectrum of foods and mechanisms including but not limited to:
- Absence of a particular enzyme needed to digest one food, e.g. lactose intolerance is caused by the lack of lactase;
- Irritable bowel syndrome, a chronic condition triggered by foods high in FODMAPs, a group of short-chain carbohydrates not digested and absorbed properly in the gut;
- Sensitivity to certain food additives, e.g. sulfite which is commonly used in wine and preserved foods;
- Recurring stress or psychological factors;
- Celiac disease, a chronic condition triggered by the consumption of gluten;
- The intensity of food intolerance may vary depending on the amount of food consumed. For example, a person with lactose intolerance may suffer from bloating after consuming a glass of milk, however, be able to enjoy a scoop of ice cream without any issue due to the difference in lactose content.
Symptoms & Reaction Time
- The symptoms of a food allergy almost always develop a few seconds or minutes after eating the food, which include:
- Tingling or itching in the mouth;
- Itchy red skin rash;
- Swelling of the face, mouth, throat or other areas of the body;
- Difficulty swallowing;
- Wheezing or shortness of breath;
- Nausea to vomiting;
- Abdominal pain to diarrhoea;
- Anaphylaxis, a set of severe symptoms including swollen tongue, breathing difficulties, tight chest, trouble swallowing or speaking, dizziness and even a collapse;
- Death in extreme cases;
- Food intolerance symptoms are never life threatening and generally less severe. While food allergies may onset immediately, food intolerance usually kicks in within a few hours of consumption:
- Stomachache, bloating, and/or diarrhoea
- Skin rashes and itching
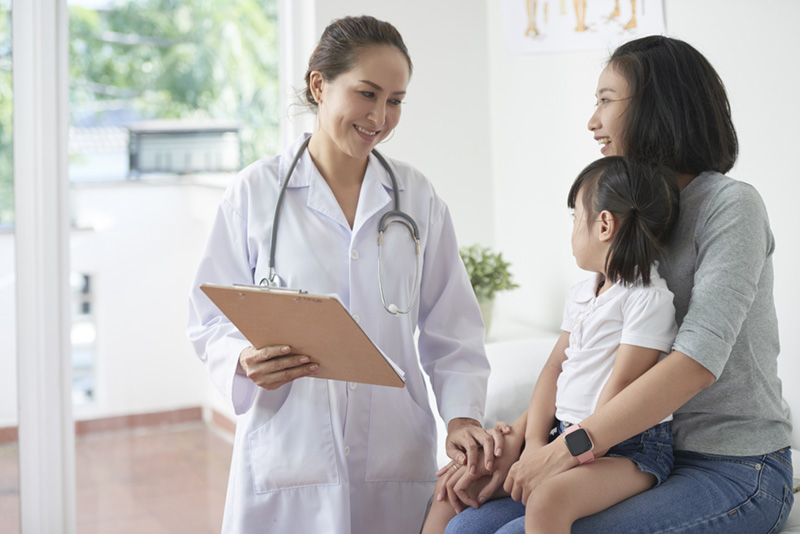
Diagnosis & Management Physiological conditions may vary among individuals. If you suspect food allergy or food intolerance in yourself or your child, please consult your physician and dietitian for a proper assessment and diagnosis in order to implement dietary adjustments to ensure safety and optimal nutrition as needed.